To Communicate Your Data Effectively With Others, First Communicate With It Yourself
During World War II, the Allies faced a critical decision: how to armor their planes for maximum protection without adding too much weight. They examined returning aircraft and found the most damage to the wings and tail, prompting them to reinforce those areas. However, mathematician Abraham Wald pointed out a flaw - the data only came from survivor planes. The ones that didn’t return likely bore damage in more vital areas, like the engines. This insight changed their strategy and, in turn, the air-to-air combat situation (Eldridge, 2024).[1]
This story highlights a key lesson: data is only as effective as it is interpreted and communicated. Whether in military or business strategy, successful decisions depend on understanding the complete picture, not just what is immediately visible. In today's world, misinterpreting or poorly communicating data can lead to failed strategies and costly mistakes. This article explores why effective data communication begins with fully understanding your data - because to communicate your data effectively with others, you must first communicate with it yourself.
Data Has Become the Backbone of Strategic Decision-Making
When entering new markets, developing innovative products, or refining operational processes, companies rely on data to inform their every step. However, data alone is insufficient, as how businesses interpret and act on it ultimately determines success or failure.
Data reduces uncertainty. For example, when a company considers entering a new market, they often rely on data to assess market demand, customer preferences, and competitor dynamics. Instead of relying on gut instincts or assumptions, data offers objective insights that help companies tailor their strategies. This same principle applies to product development, where data from customer feedback, sales trends, and competitive analysis informs design, features, and pricing strategies.
- Consider Netflix’s success in shifting from a DVD rental service to a streaming platform, thanks not only to its technology but also to its data-driven approach. By analyzing user behavior - viewing patterns, completion rates, and paused shows - Netflix curated personalized recommendations that boosted engagement. However, they went further, allowing this data to guide original content production, such as House of Cards, knowing that users favored political dramas and Kevin Spacey’s work. This calculated approach, based on data, helped Netflix produce hit content and dominate the streaming industry (Fan, 2024).[2]
Data doesn’t just describe patterns - it also creates them. This example illustrates how accurate data interpretation can shape strategic choices that position companies for long-term success. By understanding user behavior and preferences, Netflix wasn’t merely reacting to trends but actively shaping them. Data became their tool for driving both innovation and customer loyalty.
However, the success of data-driven strategies depends on the accuracy and depth of data interpretation. Misreading or miscommunicating the data can lead to costly missteps. Take the housing market crash from 2007-2008, during which the correct and incorrect data interpretation led to cardinally different outcomes:
- During the 2008 financial crisis, banks issued subprime mortgages - risky loans to people with poor credit - assuming housing prices would keep rising. They believed that if borrowers defaulted, they could repossess homes and sell them at a higher price. However, when borrowers went bankrupt, the housing bubble burst, and home prices dropped sharply. Banks repossessed homes but couldn’t sell them for enough to cover the original loan amounts. The misinterpretation of data - such as overinflated housing prices, growing risky loans, and market saturation - led to massive financial losses and a global economic collapse.
However, some investors, like Michael Burry, Steve Eisman, and John Paulson, correctly interpreted the data. They saw the unsustainable housing bubble and bought Credit Default Swaps (CDS) - a type of insurance that would pay them if the mortgages they were betting against defaulted. The sellers of CDS, including Lehman Brothers, Bear Stearns, and American International Group (AIG), thought they were making easy money, believing the market was safe and that defaults were unlikely. When the market collapsed, these institutions were obligated to pay out massive amounts while being unprepared for the scale of the defaults. Lehman went bankrupt, Bear Stearns sold at a discount, and AIG required a government bailout (FDIC, 2013). [3]
In this way, data doesn’t just inform decisions - it drives them. Successful companies take the time to deeply understand their data before making strategic moves. By communicating with their data first, they can effectively act on it, ensuring alignment and clarity in their strategies. This process ensures that decisions are data-driven, reducing the risk of miscommunication and enhancing the overall success of the company’s goals.
Common Pitfalls in Data Interpretation
But why do some fail to interpret their data? Because it requires vigilance. Common mistakes, such as confirmation bias, lead decision-makers to favor data that confirms their pre-existing beliefs, often ignoring contradictory evidence. The approach skews strategies toward comforting but faulty conclusions.
- In the late 1990s, Kodak fell victim to confirmation bias. Despite inventing the first digital camera in 1975, the company remained focused on its profitable film business, convinced, consumers would continue using film. Kodak interpreted their data in a way that confirmed their belief that film cameras and production were preferable, ignoring the growing demand for digital technology. This bias toward their then success shut their eye on the shift in consumer preferences. On January 19, 2012, one of America’s great success stories, the Eastman Kodak Company, filed for bankruptcy (Anthony, 2016). [4]
Recording assumptions before analyzing data and revisiting them afterward to ensure they haven’t influenced interpretation helps avoid confirmation bias. It’s essential to avoid cherry-picking data and to consider all evidence equally. This approach helps prevent biased conclusions and promotes more accurate decision-making.
Another issue is selection bias, where data is drawn from a non-representative sample, leading to flawed insights. For instance, a company that tests new product features exclusively with loyal customers might overestimate broader demand because loyal customers tend to be more forgiving and enthusiastic.
- In the early 2010s, Google misinterpreted market interest with the launch of Google Glass. They primarily tested the product with tech enthusiasts eager to embrace cutting-edge technology. It led Google to believe there was broad consumer demand for the product. However, the general public found Google Glass too invasive and impractical for everyday use. The reliance on a non-representative audience led Google to overestimate its appeal, resulting in the product’s commercial failure (Weidner, 2024). [5]
Mitigating selection bias requires ensuring randomized data collection and representation. It's crucial to use diverse sampling methods to gather inclusive and accurate insights, reflecting the full scope of the audience. This approach helps prevent bowed results that could lead to faulty conclusions.
Historical bias can emerge when companies use outdated data to predict future trends. Such bias can lead to strategies based on assumptions that no longer hold.
- In the early 2000s, Nokia dominated the mobile phone market. Due to relying on its past success with feature phones, they believed consumers would continue favoring hardware-based innovations, like durable phones and physical keyboards. However, Nokia ignored the new data showing that smartphones, driven by software and touchscreens, were the future. Their reliance on outdated data about consumer preferences led them to miss the rise of iOS and Android, causing them to lose their market leadership to Apple and Samsung (Wang, 2022). [6]
A practical way to avoid historical bias is by incorporating data from recent, diverse sources that reflect current social, economic, and technological changes. It's essential to acknowledge the limitations and biases within older data and orient on forward-looking, inclusive data practices that account for evolving trends. This approach ensures that strategies remain relevant and adaptable to new dynamics.
Survivorship bias occurs when focusing only on successes while ignoring failures. This selective view can lead to inaccurate conclusions about what drives success. By neglecting to analyze failures, valuable insights that could improve strategies fade.
- During the dot-com era, many companies only focused on the success of Amazon and eBay, believing that launching online businesses would guarantee success. They ignored the failures of companies like Pets.com and Webvan, which expanded rapidly without sustainable business models. Other startups, such as Boo.com, made similar mistakes by prioritizing growth over addressing logistical and market challenges. While concentrating only on success stories, they overlooked lessons from these failed ventures, leading to their eventual downfall (Wray, 2005).[7]
To avoid survivorship bias, teams should gather data from successes and failures. Considering both provides a complete picture of what works and what doesn’t. This balanced approach ensures that conclusions derive from both - fly and die cases.
Availability bias occurs when decisions are made based on the most easily accessible or recent data rather than the most relevant or comprehensive information. Such an approach often leads to contorted judgments because the data at hand, may not represent the bigger picture.
- In 2016, Samsung initially focused on a few prominent reports of battery failures in the Galaxy Note 7, assuming the problem was limited to isolated cases. Samsung reacted to the most visible data without thoroughly investigating whether the issue was widespread. The company didn’t realize that the defect affected many not-yet-reported devices. By not digging deeper into the broader problem, they underestimated the scale of the defect, leading to delayed action and a costly recall of the entire product line (Samuelson, 2016). [8]
Focusing on trends and patterns rather than vivid but isolated incidents helps prevent availability bias. Thoroughly investigating all data sources ensures a more accurate understanding of the issue rather than relying on immediately available but potentially unrepresentative information. This approach helps reveal the full scope of a problem, leading to more informed and balanced conclusions, as opposed to drawing decisions from isolated, prominent cases that may not reflect the broader reality.
Outlier bias occurs when extreme data points - significantly different from the rest - mislead the interpretation of data. These unusual data points can swerve the overall analysis, causing conclusions that do not reflect the typical patterns. The presence of outliers may result in overemphasis on rare occurrences, leading to distorted insights. Without proper context or further investigation, decisions based on outliers can overlook the trends or central tendencies of the data, potentially leading to ineffective or misguided strategies.
- In 2014, GoPro's stock surged due to the excitement around its action cameras and a viral user base, creating a sudden spike in sales and market value. This outlier event led the company to focus on expanding rapidly, assuming continued high demand. However, this was a temporary surge driven by a niche market. Over-relying on that outlier data point led to overproduction and market saturation, which ultimately caused the company stock to plummet in the following years (Victor, 2024). [9]
Mitigating the outlier bias includes full-scale data examination - often a reference to the mode and median instead of the average, and investigating any outliers without allowing them to dominate the strategy. This approach ensures that rare or extreme data points are understood in context, preventing them from sabotaging the overall analysis and leading to more balanced and accurate decision-making.
Avoiding biases such as confirmation, selection, historical, survivorship, availability, and outlier bias - along with many others - is a precursor to effectively communicating data with decision-makers. Interpreting data correctly and ensuring it is free from bias, can provide clear, actionable insights that foster alignment and well-informed strategies, ultimately enhancing decision-making processes and outcomes.
Data Only Whispers, Communication Makes It Heard Across Audiences
Effective data communication is not one-size-fits-all. Tailoring the communication style to the audience’s needs and the decision context helps convey the data insights.
Figure 1. Types of Data Communication. Source: Rogue Penguin
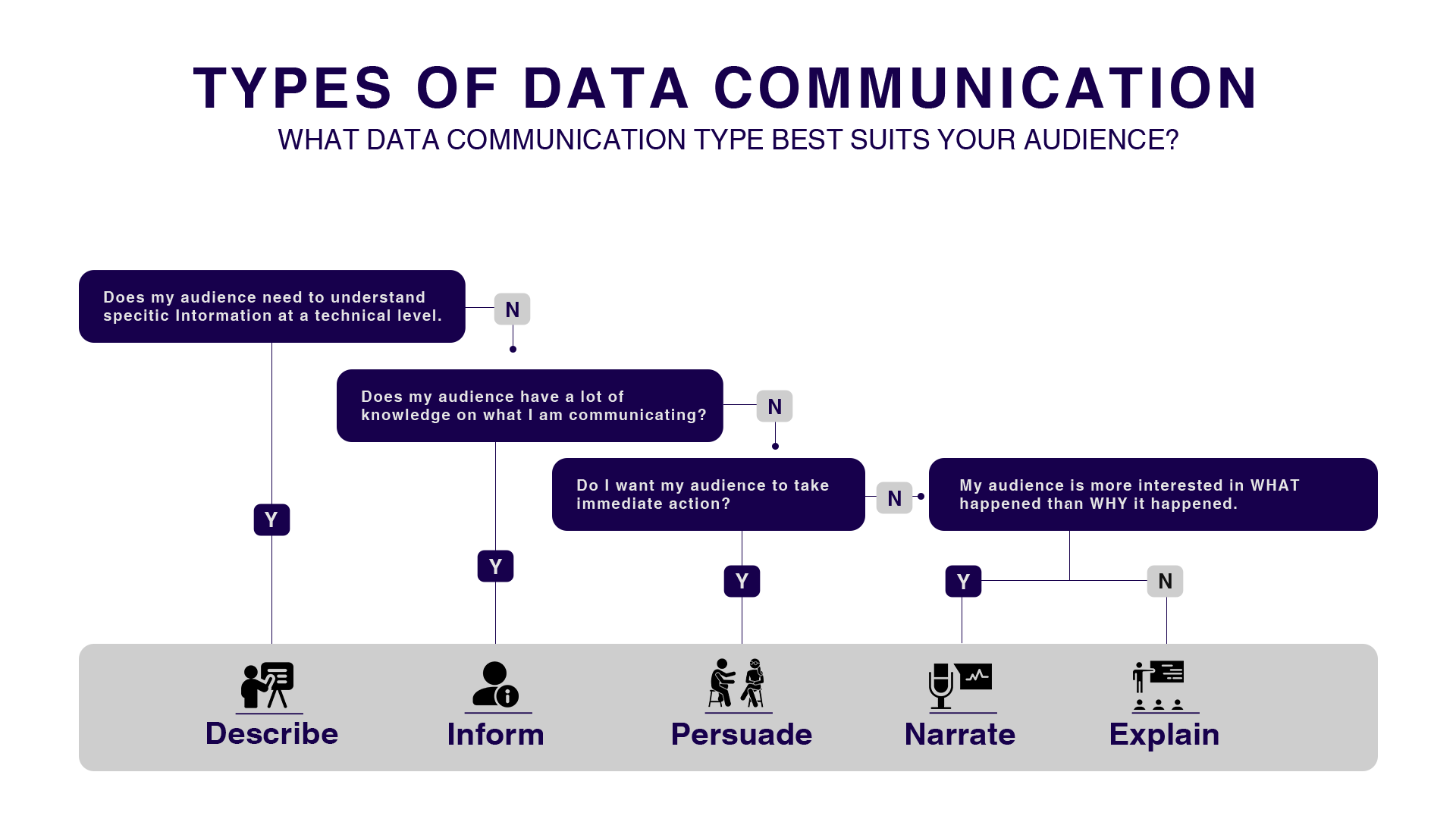
- Descriptive Data Communication: When the audience needs to understand specific technical details and has the requisite knowledge, describing the data is most effective. This method delivers detailed, granular information that explains the „what“ of the data.
- Informative Data Communication: If the audience is well-versed in the subject but doesn’t need to act immediately, an informative approach provides educational or updating data without pressing for direct action, ensuring key stakeholders remain informed about developments.
- Persuasive Data Communication: When immediate action is required, data communication must persuade. Highlighting critical insights and actionable steps connects data to decisions and motivates the audience to act.
- Narrative Data Communication: When the audience is more interested in understanding what happened rather than why, narrating data is most effective. This method weaves data into a coherent story, helping the audience follow the sequence of events leading to a specific outcome.
- Explanatory Data Communication: When the audience is less concerned with immediate technical details and wants to know why certain events occurred, an explanation is a go-to. This approach focuses on interpreting the data to provide deeper insights into the causes behind trends.
Selecting the appropriate data communication strategy and approach based on the audience's specifics is mandatory. Without this consideration, valuable data insights can remain ineffective and fail to drive informed decision-making. Tailoring the data communication strategies to the audience helps ensure that conclusions resonate, fostering better understanding and engagement.
Conclusion
Effective data communication hinges on recognizing and mitigating biases that can distort interpretation. Embracing diverse communication strategies tailored to specific audiences helps transform raw data into powerful insights. This careful consideration not only enhances understanding but also fosters informed decision-making. Ultimately, recognizing the nuances of data communication empowers us to navigate complexities, ensuring that insights resonate and lead to meaningful outcomes in an ever-evolving landscape.
References:
[1] Eldridge, E. (2024). Survivorship Bias. Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved from: https://www.britannica.com/science/survivorship-bias. October 3, 2024.
[2] Fan, H. (2024). Leader in the Digital Entertainment Market: Netflix's Continued Success in a Fiercely Competitive Environment. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences 73 (1)
[3] Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) (2013). Origins of The U.S. Financial Crisis of 2008 . Retrieved from https://www.fdic.gov/sites/default/files/2024-03/chap1_0.pdf. October 3, 2024.
[4] Anthony, D. S. (2016). Kodak’s Downfall Wasn’t About Technology. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from: https://hbr.org/2016/07/kodaks-downfall-wasnt-about-technology. October 3, 2024.
[5] Weidner, J. B. (2024). Why Google Glass Failed. Investopedia. Retrieved from: https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/052115/how-why-google-glass-failed.asp. October 3, 2024.
[6] Wang, S. (2022). Explanations to the Failure of Nokia Phone. 2022 7th International Conference on Financial Innovation and Economic Development.
[7] Wray, R. (2005). Boo.Com Spent Fast And Died Young But Its Legacy Shaped Internet Retailing. The Guardian. Retrieved from: https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2005/may/16/media.business. October 3, 2024.
[8] Samuelson, K (2016). A Brief History of Samsung’s Troubled Galaxy Note 7 Smartphone. Time Magazine. Retrieved from: https://time.com/4526350/samsung-galaxy-note-7-recall-problems-overheating-fire/. October 3, 2024.
[9] Victor, D. (2024). GoPro Stock Is at an All-Time Low. Is It a Buy? The Motley Fool & Nasdaq. Retrieved from: https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/gopro-stock-is-at-an-all-time-low.-is-it-a-buy. October 3, 2024.






