Changes in consumer needs and the business environment, as well as the rapid development of the digital environment, have revolutionized our economic and social activities in recent years. New forms of digital interaction and information exchange are challenging businesses and pushing them to embrace different digital solutions. The Covid-19 pandemic and associated economic uncertainty have brought this issue to the forefront, forcing many businesses to determine their current and future strategy on their own. To avoid value chain disruptions and meet ever-changing customer needs, companies are using digital technologies to create new digital services and business models, strengthening strategies and governance to support change. This complex combination of people, processes and technologies involved in constant change is what we can call digital transformation. Researchers agree that digital transformation is a holistic process of organizational change driven by digital technologies.
Over the decades, academics, managers and consultants have recognized that transforming organizations is difficult, and digital transformation is even more difficult, and have been trying to create different models for successful practice. They modeled the role of leaders who set a vision and unite employees around a shared vision, emphasized the importance of organizational culture in this process, demonstrated the negative impact of downward communication on digital transformation, and called on companies to listen to employees and involve them in change and create an environment conducive to the formation of new ideas. However, research shows that in most organizations, two out of three transformation initiatives fail. The more things change, the more things stay the same. ( “plus ça change, plus c'est la même chose” - Jean-baptiste alphonse karr)
In reality, most companies fail to follow established guidelines at some point in time. It is important for change managers to know how to manage change in a specific context. Understanding and analyzing different approaches to digital transformation is the best basis for managing the changes brought about by the digital context.
And yet, what is digital transformation?
The concept of digital transformation (DT) is formed by the merging of personal and corporate information technologies and includes the transformative effect of new digital technologies, such as social, mobile, analytical, cloud technologies and the Internet of things. Some researchers understand digital transformation as the integration of digital technologies and business processes into the digital economy [Liu et. al. 2011) in a relatively broad sense, DT is perceived as a driver of change in all contexts, especially in the business context, and influences the improvement of all aspects of business (Kraus et.al, 2021). More precisely, digital transformation involves three organizational aspects: improving the user experience and changing its life cycle; Optimization of business processes and changes in organizational structure, which ultimately leads to the creation of completely new business models (Benlian et al., 2016).
Digital transformation is seen as one of the most real challenges regardless of industry. Although organizations understand its fundamental importance, they still face a number of obstacles that make it difficult to initiate digital transformation, let alone reap the benefits of this transformation. (Schuchmann & Seufert, 2015)
The growing number of opportunities brought about by the development of information technology also forces companies to “systematically identify new business opportunities at an early stage” (Kiel et al., 2016, p. 675) and requires managers to adapt to one or more business models, or even creating a completely new business model. In a recent survey on digital transformation (McKinse, 2018), executives reported that their leaders are “more engaged in digital transformation than ever before,” but at the same time they said that “their companies must first solve a number of organizational problems before how digitalization can have a truly transformative impact on their business.” In this context, it can be assumed that digital transformation de facto affects all processes within the company, as it influences corporate strategies and leads to the revision and adaptation of existing business models (Linz et al., 2017). However, the extent to which digital technology adoption impacts corporate performance and can lead to innovative business models depends on the resources and capabilities available within the company, and it will take time for business models to become more context-sensitive than technology models. Therefore, it is interesting what stages a business goes through on the path to digital transformation and how these stages should be managed.
The stages of digital transformation provide companies with different opportunities at each stage. The first two stages - digitalization (also called modernization) and general business transformation - involve changing the existing business and forming it anew. And the final stage focuses on creating new business and creating more value by opening up new opportunities. (E. G. Popkova, Y. V. Ragulina, A. V. Bogoviz, 2019)
Based on various literature and research works, it can be said that organizations face difficulties in all three stages and if the company moves to the next stage without completing any of the stages, the failure rate will be even higher.
The first step (digitalization) involves simplifying and digitizing existing business processes using so-called ERP systems. This could be a customer relationship management (CRM) application, supplier relationship management (SRM) software, or other applications to optimize supply chain processes; In terms of employee experience, this could be automating HR processes or providing employees with a self-service portal, etc.
Is implementing these digital programs enough to transform an organization? - of course not. But this step is a critical foundation for organizational strength and rapid return on investment. This allows businesses to make more complex investments in their digital transformation journey.
The second stage (transformation of the entire business) is an attempt to change the complex cross-functional value chain. Steps taken at this stage for employees can be flexible transformation, creating a culture of continuous learning and development, improving the quality of customer service, this can be done by moving the product to digital channels, creating an application with integrated payment methods, delivery systems etc.
Can we call this an attempt at transformation? - Yes. Adapting the traditional organizational structure to changes, introducing appropriate management models, and taking care of talent development are the most important elements for the success of digital transformation.
Business-wide transformations typically focus on improving existing operations. But when successful, they often open up new opportunities to create value, for example by opening new markets or finding efficient new ways of doing business. That's why business-wide transformation is functional and complex, and the experience and knowledge gained at this stage is critical for companies on the path to digital transformation.
The third step (creating a new business) involves taking advantage of new opportunities to create value and create additional revenue streams. In terms of user experience, this could be the creation of a new business model, such as from selling a product or service to a subscription-based business model. On the operations side, this could be the use of data and analytics to accurately predict the operational performance of products or systems.
“To improve is to change; to be perfect is to change often.” -Winston Churchill
If we rely on neuroscientists, it is important to consider how habits are formed and how our brains respond to changing habits. To do this, companies often use the 7C model (Fig. 1), which assumes:
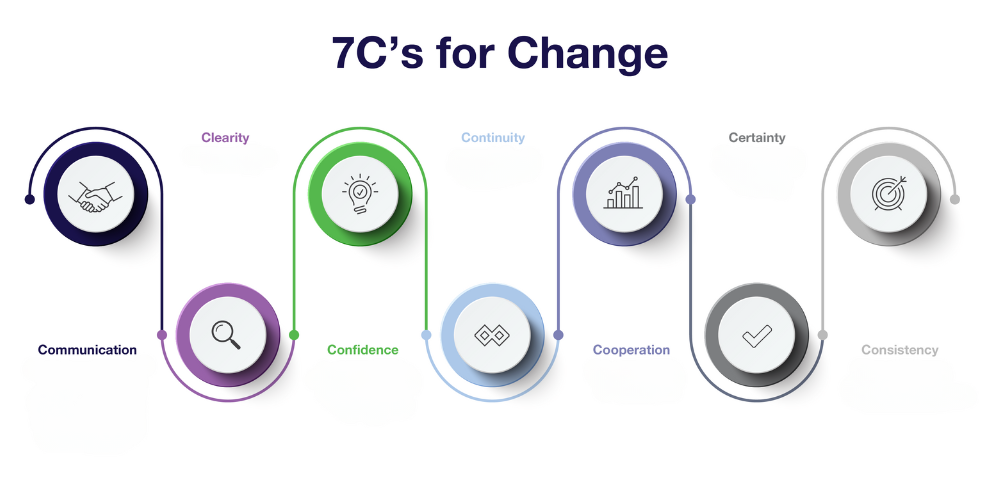
Clarity
During the transformation process, everything must be certain. To reduce risks, the roles of managers and leaders must be clearly defined. The goals of digital transformation must also be clear. Unclear goals can add to existing anxiety because employees won't know whether they've achieved the goal or how to measure their progress toward it. This means that goals must be specific and measurable. For example, a task given to employees to improve productivity could be formulated as follows: “Write four reports in the next quarter.” This way, they will know exactly what they want to achieve and identify strategies to achieve that goal.
Continuity
For effective digital transformation, this process must be continuous. This means that the conversion does not stop once it has started. Companies should plan for the next changes and get feedback on previous changes.
Employees often need time to process new information because most of the information received is quickly forgotten by the human brain. If the information is reviewed after a few days, it is much easier to retain. Therefore, when introducing digital products into an organization, training must be conducted and continually evaluated to ensure it is effective and maximizes its benefits.
Certainty
Leaders need to convey the message that digital transformation is inevitable and that the company will continue to thrive. This feeling of security and confidence will reduce threat anxiety in the brain. Communication and a sense of security will keep employees engaged in the change process, increasing the chances of success.
Consistency
There are theories that say that forming a new habit takes time. Change happens more easily when done consistently and in small doses. Leaders may want to make big changes to the company, but if they are focused only on achieving the end goal from the beginning and do not begin to implement these changes in small steps, the change process can be very difficult and painful.
Cooperation
Because the brain is a social organ, people can find comfort in interacting with others. Leaders can empower employees to create more work-oriented teams. In addition, it is necessary to involve them in the digital transformation process. Employees are more adaptable if they feel like they are the decision makers.
Confidence
Many people may feel uncomfortable in a turbulent environment when a company changes. They may doubt their competence, their abilities, etc. This can lead to increased anxiety and depression. In contrast to these feelings, leaders must ensure that their employees' self-esteem increases. They need to show that employees themselves control the processes, make choices about what tactics to use to achieve the goal, etc.
Communication
Communication is key when it comes to transformation. Employees want to feel like they have a voice and that their voice is understood. When making changes, it is necessary to create platforms where employees will have the opportunity to share their opinions and be part of the changes as much as possible. Leaders must show empathy during stressful times and connect with employees on an emotional level. This communication can take the form of surveys, feedback sessions, or one-on-one conversations.
How should companies make the technological changes that differentiate successful digital transformation from the rest?
True transformation requires new ways of working, in which leadership plays a critical role as it involves moving from an existing operating model to a new one. Therefore, it is extremely important to have leaders who are well-versed in modern technology.
It is recognized that the top management of a company is responsible for the major strategic decisions of the organization. Senior management involvement in driving digital transformation and innovation management is an important part of corporate commitment to a company's strategic efforts and is positively correlated with the successful implementation of digital initiatives. Involving executives in transformation is critical because their specialized knowledge, skills, and experience are typically the greatest and most important organizational resources. Existing experience reveals the role of the executive, especially in conditions of high uncertainty.
One of the most important roles of chief executive officers (CEOs) is to mobilize employees to contribute to the company's strategic goals. In recent years, the concept of transformational leadership has become relevant, which promotes intellectual stimulation, creates idealized influence, inspires motivation and stimulates innovative growth. Transformational leaders manage to initiate reforms in the organization at a strategic level, inspire and guide people towards these changes. These leaders create organizational culture by placing greater emphasis on a shared vision, which leads to shared values between the company and its employees. In an organizational culture with such shared values, achieving a common goal is achieved much more effectively than in companies where there is no agreed-upon vision. Organizational development researchers argue that transformational leaders play a key role and have a significant impact on organizational culture and values. The role of leaders in bringing about change in their companies is essential, which means that without leadership there can be no change. They play a decisive role in accelerating or slowing down organizational change, so their tasks during a change management strategy can be formulated as follows:
Develop an organizational culture that encourages innovation at all levels. Creating an organizational climate that supports innovation and change is an important step forward for companies. Human capital, which is unique to every organization, needs to be encouraged. Management must address two broad issues. First, leaders need to understand the impact of their role behavior on digital transformation stakeholders. The second factor is the ability of leaders to cope with high levels of uncertainty while simultaneously stimulating innovation.
Digital transformation is impossible without thinking outside the box. Attention to creativity and divergent thinking has been especially focused in the 21st century, when the development of information technology has revolutionized our lives, work processes, communication, behavior, etc. Today, pragmatic and straightforward decisions are no longer valued as highly as they were during the development of manufacturing. According to research, as people reach adulthood, divergent thinking decreases, so people begin to think routinely and repeat what they have learned. Therefore, in the workplace, it is the responsibility of leaders to encourage the generation of original ideas and creative thinking. Since employees are given the freedom to innovate their tasks, it leads to both motivation and enthusiasm to work consistently and achieve innovative goals. The only serious problem with this process occurs when it is not supported by a strong value system in the organization that can guide activities in accordance with the overall goals of the organization.
Set short-term goals and celebrate small victories. Successful and sustainable digital transformation takes time, which means the distant prospect of an end goal may not motivate employees. Therefore, leaders must create an environment conducive to early success and visible improvement. Small achievements like these make many people feel enthusiastic and motivate them to do better.
Making transformation a personal goal. People are generally more enthusiastic about something when they think it was their idea than when they are assigned to do it. Therefore, if managers care more about a particular initiative, employees perceive it as their own. However, when employees understand how digital transformation improves their work processes, it becomes clear that their contribution to achieving the transformation goal increases.
Monitoring progress is not only beneficial for all stakeholders involved in a digital transformation project, but is also critical to strategy development. Key performance indicators and transformation management indicators highlight strategy weaknesses. By understanding what works and what doesn't, leaders can adjust the plan.
Too often, senior management forgets that they are not the only role models influencing employees; Informal leaders in organizations may have less influence on the energy levels of their colleagues if they are excited about the change agenda. Regardless of their official title and status, attracting such people increases the likelihood of change success by 3.8 times.
Here are steps companies can take during transformation to increase their chances of success:
- Rethinking the workplace. Successful digital transformation requires both digitally savvy leaders and the human capital to drive digital transformation change. Of course, companies will have to invest to develop radically different skills and abilities among employees or to hire new talent, but without this, change is impossible. One of the most important steps for organizations is to develop clear working capital strategies that will help identify the digital skills and capabilities they currently have and will need to achieve their future goals.
- Renewing the organization's culture. As digital transformation requires new ways of working, as well as changes to the overall culture of an organization, employees must be able to work differently and keep up with the faster pace of business. The introduction of digital tools and renewal processes, as well as the development of a flexible operating model, will facilitate these changes.
- Changing old ways of communication. Good communication has always been a key success factor in traditional change efforts, and it is no less important in digital transformation. In a digital context, companies must use more creative channels to enable new, faster ways of working and faster changes in thinking and behavior that digital transformation requires. One shift is a shift from traditional channels that support only one-way communication (such as company-wide email) to more interactive platforms (such as internal social media) that open the door to open dialogue within the organization.
References:
Liu, D.Y., Chen, S.W., Chou, T.C. (2011) Resource fit in digital transformation: lessons learned
from the CBC Bank global e-banking project. Manag. Decis. 49(10), 1728–1742
Kraus S., Jones P., Kailer R. , Weinmann A., Chaparro-Banegas N., and Roig-Tierno N. (2021) Digital Transformation: An Overview of the Current State of the Art of Research
Benlian T. H., A., Matt, C., Wiesböck, F. (2016) Options for formulating a digital transformation strategy. MIS Q. Exec. 15(2), 123–139
Schuchmann, D., Seufert, S. (2015) Corporate learning in times of digital transformation: a conceptual framework and service portfolio for the learning function in banking organizations. Int. J. Adv. Corp. Learn. (iJAC) 8(1), 31–39
Kiel, Daniel & Arnold, Christian & Collisi, Matthias & Voigt, Kai-Ingo. (2016). The Impact of the Industrial Internet of Things on Established Business Models.
Dr. Linz, Carsten & Müller-Stewens, Günter & Zimmermann, Alexander. (2017). Radical Business Model Transformation: Gaining the Competitive Edge in a Disruptive World.
https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/business%20functions/people%20and%20organizational%20performance/our%20insights/successful%20transformations/december%202021%20losing%20from%20day%20one/losing-from-day-one-why-even-successful-transformations-fall-short-vf.pdf
https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/digital-transformation-on-the-ceo-agenda






